Does your project really needs blockchain?

In today’s business world, blockchain has become a real hype, causing thousands of businesses to pour money into this technology. Everybody know that blockchain is trendy and that it is used by many industries all over the world.
But does everybody really understand what blockchain is, and when exactly it makes sense?
In 2017, the investments in blockchain reached about $3 billion and by 2021 the blockchain tech market all over the world will reach $2.3 billion, according to Statista. But do you really have to succumb to the moment? Not necessarily.
We normally spend our money on something that will be beneficial for us in the future – but do all those who are dreaming to make something utilizing blockchain really analyze the technology's potential and its future impact on the business?
While talking to customers in UAE we faced the situation for a few times that the goals of the customer’s ‘another huge blockchain sensation project’ could be solved without even using the blockchain. And sometimes blockchain didn’t make sense at all as a solution for the project goals.
So the important thing here is to carefully analyze the blockchain potential and compare it to your existing technologies. The questions is not “how cool the blockchain is” but “what benefits and advantages can it bring you comparing to other technologies, or what problems blockchain can solve that other technologies cannot?”
Understanding the core
First of all, let’s see what blockchain is.

The blockchain is a digital ledger of economic transactions that can be programmed to record virtually anything of value, according to Don & Alex Tapscott, authors Blockchain Revolution (2016).
There are two types of blockchain: public and private. When every transaction is transparent and its record is available to the public, it is correspondingly called a public blockchain. When the ledger has to be more private, like B2B sales, this is what private blockchain is.
So what does blockchain technology do and what benefits does it have?
First of all, it allows distributed processing power. Secondly, the ledger turns into an implicit record of transaction. This leads to the third benefit – two parties can engage into transaction without the need to call for the third party.
All these advantages are real and are the reasons for the blockchain popularity. However, any investment calls for assessment first, meaning, you have to see not only the pros of the technology but its flaws as well.
When you don’t need blockchain
Since we spoke about its advantages, we will know play the devil’s advocate and asses them from the competitive point of view.
You don’t need blockchain when you don’t need decentralization. If we speak about bitcoin, here decentralization is a must-have. The currency is not influenced by the government and this is how it’s meant to be.
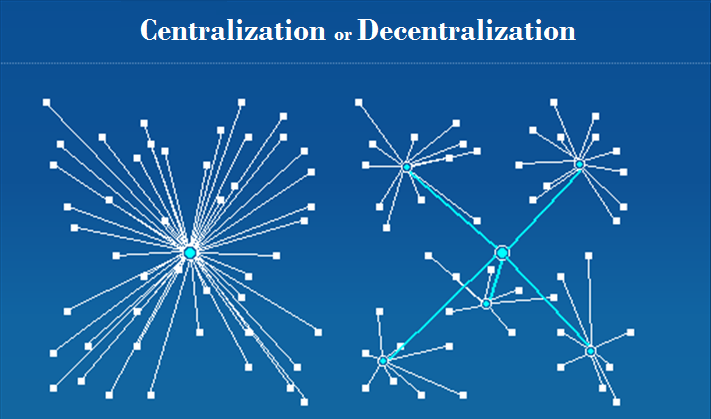
However, great number of products and services are offered by the central party aka retailer and that’s completely normal.
At times central authority is needed, for example, to handle the requests by setting up centralized services. YouTube is a perfect example of such centralized service. Yes, it can use blockchain – but would it really be a good idea if we already have a central authority?
Next comes the question of distributed processing.
Do we really need it when processing power is so cheap? Let’s have a look at the costs for GFLOPs processing (one billion floating-point operations per second). Back in 1984 processing of 1 billion operations would cost about $ 18.5 billion. Now it costs 6 cents only.
Some may say: what about the processing power of companies-giants like Amazon?
Such companies have enormous processing farms and they also have access to vast resources so for them the question of processing power cost does not matter much. And today, being able to afford high-end PCs and various server solutions, researchers and scientists also save their money, not having to spend them on expensive servers.
And don’t forget about the storage costs. $11 500 vs 2 cents for the gigabyte of storage in 1990 and 2016. So overall, blockchain would not be much of a money-saver for you in terms of data storage and processing costs.
Digital contracts/ smart contracts - for some reason the hype is associating them with blockchain. In some cases smart contracts with blockchain can benefit and be part of a bigger blockchain project, but it doesn't make much sense by its own. The paperless documents is a task that have already been solved before. Same is true for supply chain management or record tracking - even though blockchain is an efficient tool for solving such tasks, it’s not the irreplaceable one.

Last but not least - the question of identity. Blockchain is useful when the parties are unknown and are mutually mistrusting. Blockchain verifies each party carefully and the transaction does not occur until both buyer and seller complete the verification process.
However, there is not much use for blockchain when parties are known. If something goes wrong between the two businesses, it will call for legal action and the matter will be resolved.
Blockchain flaws
Despite being a somewhat revolutionary technology, blockchain still has its flaws. One of the biggest is a “51% attack” – a potential attack on the bitcoin network in case some organization somehow manages to control the majority of the network mining power.
And if we look at massive blockchains, imagine how much processing power would be required to pull the attack off?
Also once again think about identity. Once the bitcoin is stolen, you lose it forever and you don’t know the identity of the hackers. In addition, once the ledger transfers the bitcoin to a new party, the transaction is considered official – and nothing you can do about it.
So the question of security causes serious concerns about deploying blockchain and this is another reason many organizations still hold back from using it.
To sum up, blockchain has its pros and cons, same as any other technology. It’s invaluable for some applications and for others there is a better alternative than blockchain.
So before following the hype and rushing into blockchain investment, perform the analysis of your business and estimate the competitive advantages of blockchain before using it.

Conclusion
What we are saying here is not that blockchain is bad - we rather want to say that it’s not a universal solution for every issue out there. Due to the hype around it many people consider blockchain a win-win solution but at times there are cheaper tools of same efficiency.
The biggest problem that blockchain solves is the problem of trust between the parties. It also serves as a plenary record of transaction and eliminates third party from it - and basically these are the biggest blockchain benefits.
But hey, maybe you are really into experiments and are willing to try the new technology! Can’t blame you for that but keep in mind that blockchain is the most consuming technology in terms of implementation.
Nevertheless, a creative person will always find new cases for blockchain implementation and this is especially true for Dubai where a lot of support for blockchain is shown. But before choosing blockchain as a key solution, one should know the basic technology principles and have deep understanding and knowledge of the problem to be solved.